Question: 1 -
Traffic light System is the example of:-
-
None of these
-
Open-loop System
-
Closed-Loop System
-
Both (1) and (2)
Answer:
Open-loop System
Solution:
The Traffic lamp will glow according to the set of timing and sequence and is time-dependent. The sequence and time are controlled by relays that work on the preprogrammed time. it does not depend upon the rush of the road.
Hence the Correct answer is (1)
The Traffic lamp will glow according to the set of timing and sequence and is time-dependent. The sequence and time are controlled by relays that work on the preprogrammed time. it does not depend upon the rush of the road.
Hence the Correct answer is (1)
Question: 2 -
Loop gain is equal to:
-
Product of all branch gains in a loop
-
Product of all branch gains while traversing the forward path
-
Summation of all branch gains in a loop
-
Sum of all branch gains while traversing the forward path
Answer:
Product of all branch gains while traversing the forward path
Solution:
According to Mason's Gain formula, the transfer function can be calculated as:
T(s) = C(s)/R(s)
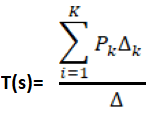
Where,
Pk is the forward path gain
∆istheloopgain, which is calculated as:
∆=1-∑(Allloopgain) + ∑(Gainproductoftwonon-touchingloops)-∑(Gainproductofthreenon-touchingloops)
∆k iscalculatedbyeliminatingallloopstouchingPk
Here, the loop gain is defined as the product of the branch gain that is traversing a forward path.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (2).
The Mason's gain formula is used to find the overall transfer function of a signal graph.
According to Mason's Gain formula, the transfer function can be calculated as:
T(s) = C(s)/R(s)
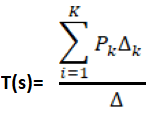
Where,
Pk is the forward path gain
∆istheloopgain, which is calculated as:
∆=1-∑(Allloopgain) + ∑(Gainproductoftwonon-touchingloops)-∑(Gainproductofthreenon-touchingloops)
∆k iscalculatedbyeliminatingallloopstouchingPk
Here, the loop gain is defined as the product of the branch gain that is traversing a forward path.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (2).
The Mason's gain formula is used to find the overall transfer function of a signal graph.
Question: 3 -
The Static system can be defined as:
-
Output of the system depends on future inputs.
-
Output of the system depends only on the present input.
-
Output of a system depends only on the received inputs.
-
Output of a system depends on the present as well as past input.
Answer:
Output of the system depends only on the present input.
Solution:
Static systems do not have any feedback system. Hence, the output depends only on the present input.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (4).
Static systems do not have any feedback system. Hence, the output depends only on the present input.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (4).
Question: 4 -
A major part of the automatic control theory applies to the:
-
Casual systems
-
Non-linear systems
-
Time variant systems
-
Linear Time invariant systems
Answer:
Linear Time invariant systems
Solution:
A linear time invariant (LTI) system provides the same output for the same input irrespective of when input is given. LTI systems are also used to predict the system's long term behavior.
Hence the correct answer is an option (b).
A linear time invariant (LTI) system provides the same output for the same input irrespective of when input is given. LTI systems are also used to predict the system's long term behavior.
Hence the correct answer is an option (b).
Question: 5 -
If the characteristic equation of the closed loop system is s^2 + 2s + 2 = 0, then the system is:
-
Underdamped
-
Undamped
-
Over damped
-
Critically damped
Answer:
Underdamped
Solution:
Kindly Compare the given charateristic equation with the standard form of second order differential equation.
Kindly Compare the given charateristic equation with the standard form of second order differential equation.